Looking back, looking forward

Yesterday’s group Xmas party (a bit early in the season, granted, as some of the team are off today to visit CCA at the Flatiron Institute) was the opportunity to thank everyone in the group for a great year together.I am grateful not only for the science we did together with these young and talented […]
Machine learning pipeline for direct detection experiments
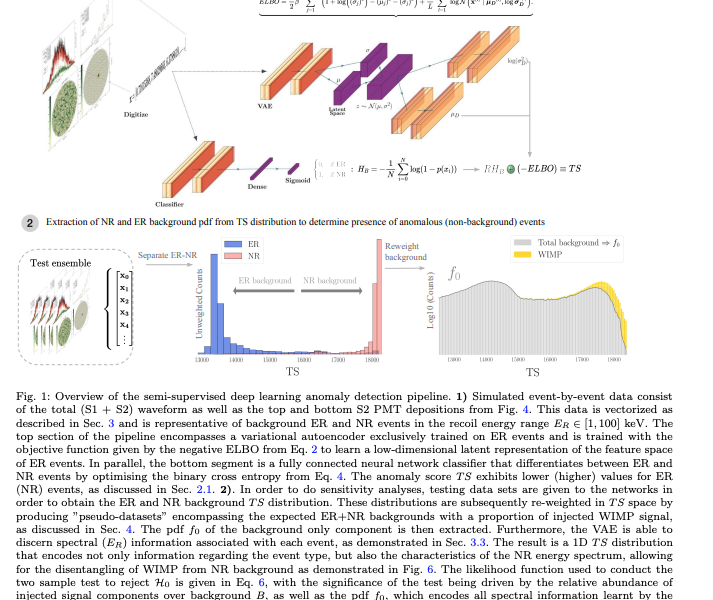
After painstakingly thorough work, I am pleased to see our new paper, led by Andre Scaffidi, out today as part of the DARWIN direct dark matter detection collaboration! 👏 We use a semi-supervised anomaly detection pipeline, comprising of a variational autoencoder trained on simulated background events and a classifier distinguishing between electronic and nuclear recoils, […]
The impact of Machine Learning in Cosmology
An online debate hosted by the Machine Learning Club, with co-panelists Bhuvnesh Jain, Uros Seljak and Hiranya Peiris, held on Apr 28th 2021.
Inaugural lecture: From the Big Bang to AI
My inaugural lecture as Professor of Astrostatistics at Imperial College London on Jan 15th 2020. A truly unique opportunity for me to sum up what I’ve learnt, from dark matter to Bayes, to the the audience to taste dark matter and feel the dark matter wind (!) and to share the journey. An unforgettable, emotional […]
Today on the arXiv: Light echo gives insight into SNIa dust environment
I noticed this interesting paper using high resolution, multi-epoch images from Hubble to study the time evolution of the aftermath of the explosion of SNIa SN204J, which went off in 2014 in the nearby galaxy M82 (a mere 11 million light years away). The data show the presence of a radially expanding light echo, as well […]
Today on the arXiv: how to measure the intrinsic CMB dipole, and radio emission from DM in the Coma cluster
Elena Pierpaoli and her collaborator Slavash Yasini come up with a clever way of measuring the intrinsic CMB dipole, and disentangling it from the much bigger dipole induced by the Earth motion with respect to the CMB rest frame. The key idea is that leakage of the intrinsic dipole into the monopole and quadrupole induces […]
Today on the ArXiv: How to ride a light beam to the stars, and how not to analyse distance indicators
Today on the arXiv, a nice analysis of how to design a solar sail in such a way that the light beam powering it is prevented from rocking it side to side, and hence destabilising it. The key idea is to use a spherical sail (rather than conical designs as previously proposed) and a multi-modal laser […]
Today on the arXiv: Prospector-alpha opens the way to high-accuracy photometry-based estimation of galactic properties
There is a terrific paper on today’s arXiv: The Prospector-alpha code is an impressive new approach to estimating a large number of important physical parameters of galaxies, including indicators for the galaxy’s star formation history, its metallicity, its mass and dust content. The code contains a large number of free physical parameters (describing star formation […]
Today on the arXiv: from light bulbs to 2 trillion dark matter particles simulations in 75 years
Today, Martin White suggests using a density-dependent correlation function as a tool to help distinguish General Relativity from modified gravity theories. The N-body simulation Zurich group shows impressive results from a cosmological simulation involving 2 trillion (2 x 10^12) particles, which they run on the Swiss Supercomputer in Manno using GPU-accelerated nodes, and benchmarked with […]
Bad news for LISA and Dark Matter line emission from the Galactic Centre
Today on the arXiv (arXiv:1609.08093) Camille Bonvin and collaborators (whom I know well from my days in Geneva) rule out the possibility to use the distortion in the gravitational waves chirp signal to measure the acceleration of the universe. They find that the peculiar acceleration is much greater and therefore would (1) wash out the […]
